In India, there are three banks- SBI, HDFC Bank, and ICICI Bank classified as D-SIBs, meaning their failure can impact the financial stability and create instability in the country.
These banks have become “too big to fail” and are widely recognized as the core of the Indian economy. For example, the State Bank of India (SBI) has an extensive customer base of over 48 crores. Given its massive influence, any disruptions or adverse events concerning the bank can significantly impact the nation’s financial stability.
In this article, we will do a fundamental analysis of SBI and check the long-term growth potential of SBI share price.
SBI Company Journey
State Bank of India is a Fortune 500 company with a legacy of over 200 years and is currently the most prominent Indian bank by assets, with over one-fourth market share.

Over the years, the State Bank of India has established its presence with the greatest number of branches and ATM networks across India. At the end of Q4 FY23, SBI had 22,405 branches and 65,627 ATMs nationwide. It has established an international presence in 29 countries.
Merger of SBI Subsidiaries
On 13th August 2008, the State Bank of India embarked on another journey toward unifying the Indian banking system by merging all its subsidiary banks.
In 1959, the government passed the State Bank of India (Subsidiary Banks) Act in parliament, bringing the eight banks belonging to princely states as State Bank of India subsidiaries. The banks include:
- State Bank of Jaipur
- State Bank of Bikaner
- State Bank of Saurashtra
- State Bank of Indore
- State Bank of Travancore
- State Bank of Mysore
- State Bank of Patiala
- State Bank of Hyderabad
State Bank merged all its associate banks with itself on 1st April 2017. This helped SBI to break into the club of the top 50 largest banks in the world.
Subsidiaries of SBI
State Bank of India has firmly established itself as a key player in India’s financial landscape, providing its customers a wide range of financial products and services through its subsidiaries. The key subsidiaries of SBI include:
- SBI Card
- SBI Life
- SBI General Insurance
- SBI Mutual Fund
- SBI Caps
SBI Company Analysis
State Bank caters to the diverse needs of individuals and businesses, offering an extensive range of products and services covering a broad spectrum of financial requirements. It provides services in;
- Personal Banking
- Rural Banking
- Corporate Banking
- SME Banking
- International Banking
- Digital Banking- YONO
It has categorized its business operations into four primary segments:
- Treasury
- Corporate/ Wholesale Banking
- Retail Banking
- Other Banking Businesses
In the fiscal year 2022-23, State Bank demonstrated robust financial performance. Net Interest Income (NII) jumped to ₹1,44,841 crores, marking a significant growth of 19.99% compared to the previous fiscal year. Additionally, the bank recorded a net profit of ₹50,232 crores, showcasing a substantial year-on-year surge of 58.58%.
SBI Management Profile
- State Bank is led by Chairman Shri Dinesh Kumar Khara, appointed on 7th October 2020, for three years. He joined SBI as a probationary officer in 1984.
- Shri C.S. Shetty, Managing Director, leads the International Banking, Global Markets & Technology division.
- Shri Swaminathan Janakiraman, Managing Director, leads the Corporate Banking & Subsidiaries.
- Shri Ashwini Kumar Tewari, Managing Director, oversees the Risk, Compliance, & SARG division.
- Shri Alok Kumar Choudhary, Managing Director, leads the Retail Business & Operations.
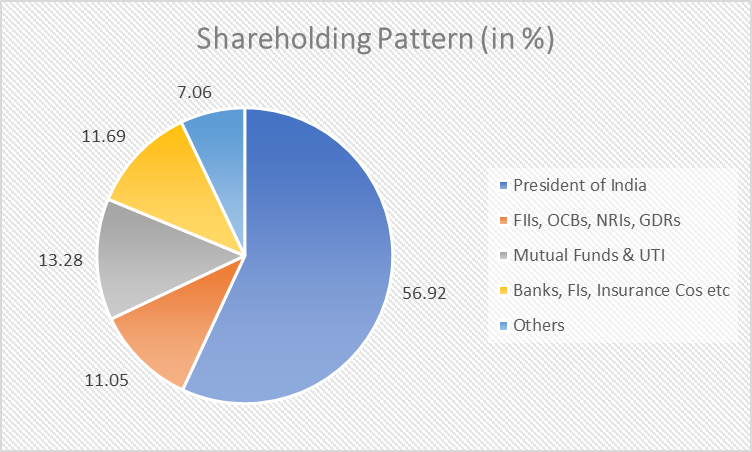
SBI Shareholder Pattern
SBI Financials
Revenue
In FY23, SBI reported a total income of ₹3,68,719 crores, up 16.68% over FY22 at ₹3,16,021 crores.
The bank’s non-interest income of ₹36,616 crores during FY23 is 9.73% lower compared to the previous fiscal mainly because of a fall in forex income and loss in the sale of investments.
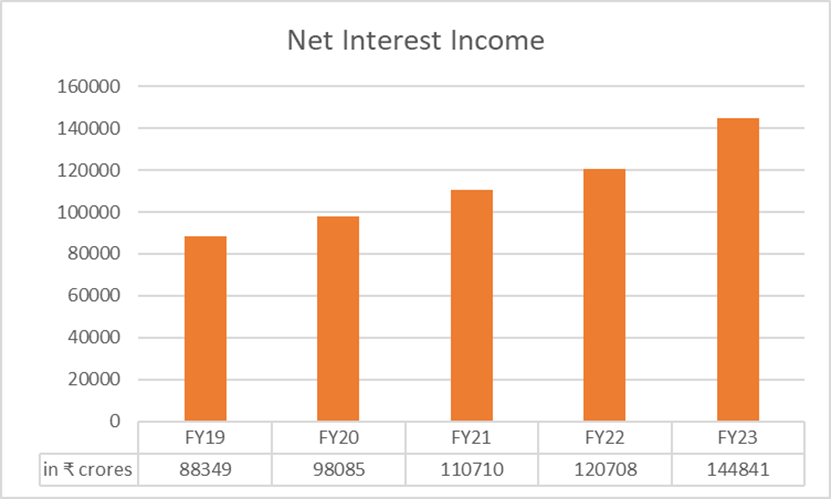
Net Interest Income (NII)
SBI reported robust growth in NII during FY23 on account of increased lending rates and healthy credit growth. The bank’s NII grew by 19.99% to ₹1,44,841 crore from ₹1,20,708 crore in FY22. The bank’s NII has grown at a CAGR of 10.39% in the last five years.
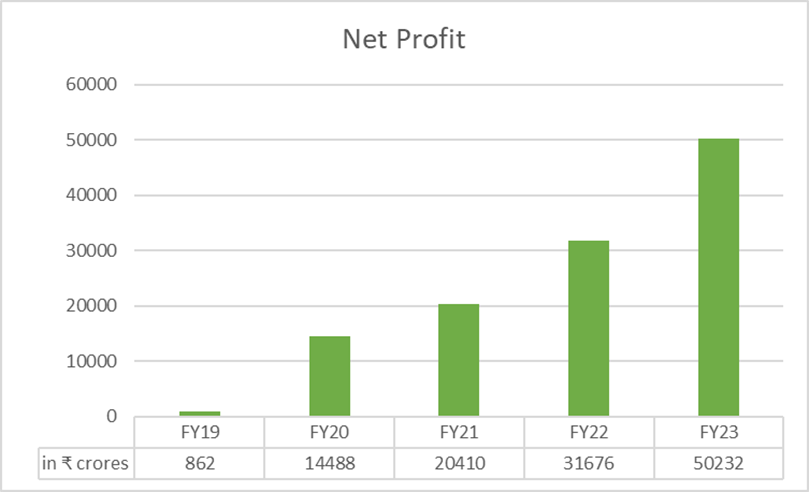
Net Profit
In FY23, SBI reported a 58.58% growth in net profit to ₹50,232 crores compared to the previous fiscal at ₹31,676 crores. In the last five years, banks’ Net profit has grown at a CAGR of 125.47%.
SBI Key Financial Metrics
Non-Performing Asset (NPA)
In FY23, the bank’s net NPA improved by 35 bps to 0.67%, indicating better asset and risk management to prevent slippages and loans from turning bad.
The bank’s net NPA ratio has decreased by 234 bps over the last five years from 3.01% in FY19.
Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR)
The overall Capital Adequacy Ratio at the end of March 2023 is 14.68% against the minimum regulatory requirement of 12% for public sector banks.
A higher CAR indicates that the bank is well insulated to absorb any shock like a spike in bad debt accounts.
Provision Coverage Ratio (PCR)
PCR signifies the funds a bank allocates to mitigate potential losses arising from non-performing or bad debts. SBI’s PCR, excluding AUCA, at the end of March 2023 is 76.39% compared to 75.04% in March 2022.
CASA Ratio
CASA represents the Current and Saving Account Ratio represents the percentage of deposits in current and saving accounts to total deposits.
At the end of March 2023, SBI’s CASA was 43.80% compared to 45.28% in March 2022. Despite the decline in the CASA ratio, the bank’s total CASA deposit rose 4.95% to ₹18,62,904 crores at the end of FY23.
A higher CASA ratio indicates a lower cost of funds for banks since they do not pay interest rates on current accounts and typically offer relatively lower interest rates on savings accounts.
Cost of Funds
The bank’s credit cost in FY23 decreased by 23 bps to 0.32% from 0.55% in FY22. It played a crucial role in enhancing the profitability of the bank.
Net Interest Margin (NIM)
The NIM improved to 3.37% at the end of FY23 from 3.12% at the end of FY22.
SBI Share Price Analysis
After experiencing a period of consolidation and relatively weaker performance compared to private lenders, the share price of SBI has undergone a remarkable turnaround in recent years.
As of 5th June 2023, the bank’s market capitalization stands at ₹5,24,053 crores. SBI share price has delivered an impressive compound annual growth rate (CAGR) return of 46% between 8th June 2020 and 5th June 2023. SBI share price has increased from ₹169.80 to ₹583 during the period.
In December 1993, SBI launched its IPO at a premium of ₹90 per share, with a face value of ₹10. Notably, in October 1996, SBI became the first Indian bank to issue Global Depository Receipts (GDR).
SBI shares underwent a split in the ratio of 1:10 on 20th November 2014, and the current face value is ₹1.
Over the past three years, the bank has consistently increased its dividend payout, reflecting its commitment to rewarding shareholders. The dividend per share has risen from ₹4 in 2021 to ₹7.10 in 2022 and further to ₹11.30 in 2023.
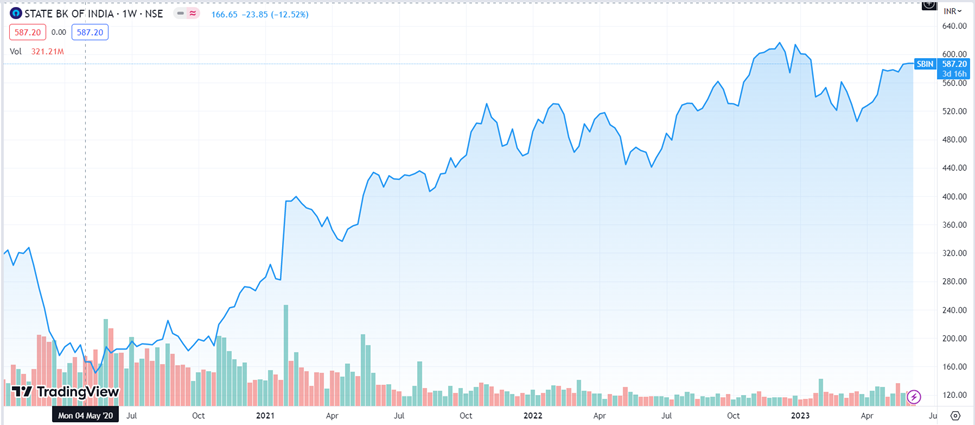
The SBI share price was trading around the ₹149.5 level in May 2020 and made an all-time high of ₹629.55 on 12th December 2022.
SBI Share Price Fundamental Analysis
FY23 has marked a significant turnaround in performance for the State Bank of India, making it one of the most successful years in the bank’s history.
Credit Growth: In FY23, the bank maintained strong growth in advances at 15.99% to ₹32,69,242 crores and has held leadership across all segments in the retail and personal segment. The bank’s market share in home loans is 33.1%, and auto loans are 19.1%.
Overall, SBI has a high-quality asset book with 82% exposure to A, AA, AAA rated debt, thereby reducing the chances of slippages.
Strong Growth in NII: Supported by the combination of lower credit costs, enhanced lending rates, and strong credit growth, the bank achieved robust growth in Net Interest Income (NII), registering an impressive increase of 19.99%.
Improving Asset Quality: In FY23, fresh slippages are lower than recovery from stressed assets which has helped SBI to improve GNPA and NNPA ratios.
In FY23, the slippages are down by 26.38% y-o-y, and there is a decline in the restructuring of loan accounts.
Deposit Mobilisation on Par with System Growth: The bank’s CASA grew by 4.95% in FY23.
The overall domestic deposit, including term deposits, grew by 8.5% to ₹42.53 lakh crores, and foreign office deposits grew by 29.60% to ₹1.70 lakh crores.
Current Account deposits grew by 7.47%, and Savings Account deposits grew by 4.51%.
SBI has experienced a slight uptick in the cost of domestic deposits, reaching 3.99% by the end of March 2023 compared to 3.88% in March 2022. However, the bank anticipates a stable outlook for the cost of deposits and does not foresee any significant increases shortly.
Healthy Credit Growth Outlook: After the release of Q4FY23 earnings, the bank has given a 12% to 14% loan growth in FY24. The bank doesn’t foresee any sharp uptick in loan growth in coming quarters due to the high base effect.
Retail loans constitute 36% of the bank’s total gross advances and are growing without much challenge, and strong growth is witnessed in the Xpress Credit segment with 22.72% y-o-y growth in loan outstanding. In the corporate segment, loan disbursement to the SME segment is also accelerating.
Digital: The bank’s digital strategy is witnessing strong growth, with 64% of savings accounts and 35% of retail asset accounts acquired through YONO in FY23.
YONO has over 6 crores of users, which gives the bank a superior capability to cross-sell its products, and the online marketplace, which has 100+ partners, helps to generate commission income. The platform is witnessing a daily average of 550K transactions and 10 million daily logins.
SBI Share Price Growth Potential
The State Bank of India’s share price is poised to benefit from evolving scenarios, supported by robust Goods and Services Tax (GST) collections reported in the first two months of FY24 and the anticipated GDP growth of 6.5% in the current fiscal year against uncertain global economic conditions.
Factors that are likely to support growth in SBI share price:
- Lower cost of funds compared to peers
- Healthy credit growth outlook in FY24
- Improved asset quality
- Digital strategy paying a strong dividend
The combination of these factors is highly conducive to sustaining the growth momentum of the State Bank of India. As a result, the SBI share price is anticipated to experience a significant upward trajectory over the long term, reflecting the positive market sentiment and the bank’s strong performance indicators.
*Disclaimer Note: The securities quoted, if any, are for illustration only and are not recommendatory. This article is for education purposes only and shall not be considerea d as recommendation or investment advice by Research & Ranking. We will not be liable for any losses that may occur. Investment in securities market are subject to market risks. Read all the related documents carefully before investing. Registration granted by SEBI, membership of BASL, and certification from NISM in no way guarantee the performance of the intermediary or provide any assurance of returns to investors.
FAQs
When was SBI founded?
SBI is the country’s oldest bank and was first established as the Bank of Calcutta in 1806 and three years later renamed as Bank of Bengal.
In 1921, the amalgamation of the Bank of Madras, Bank of Bombay, and Bank of Bengal led to the creation of the Imperial Bank of India. And in 1955, After RBI took control of the Imperial Bank of India, renamed as State Bank of India.
How SBI share price has performed in the last five years?
As of 5th June 2023, SBI share price has given a CAGR return of 17% in the last five years.
Who owns SBI?
SBI is a public sector bank, and the Government of India holds a 56.92% stake in the bank.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 3.8 / 5. Vote count: 25
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.