Introduction Punjab National Bank, popularly known as PNB Bank, became the third bank in the public domain to reach a
Continue reading
Fundamental analysis of stocks based on the quarterly and annual reports of the companies.

Introduction Punjab National Bank, popularly known as PNB Bank, became the third bank in the public domain to reach a
Continue reading
Indian Railways is not one organization but a combination of multiple organizations dedicated to the daily operations and functioning of
Continue reading
Several brands have ingrained themselves so deeply in our lives that they have become nearly irreplaceable or synonymous with their
Continue reading
Bank of Baroda’s history is steeped in excellence as one of India’s foremost public sector banks. With a robust legacy,
Continue reading
Did you know Colgate originally sold soap and perfume before adding toothpaste to their product portfolio? The company’s roots date
Continue reading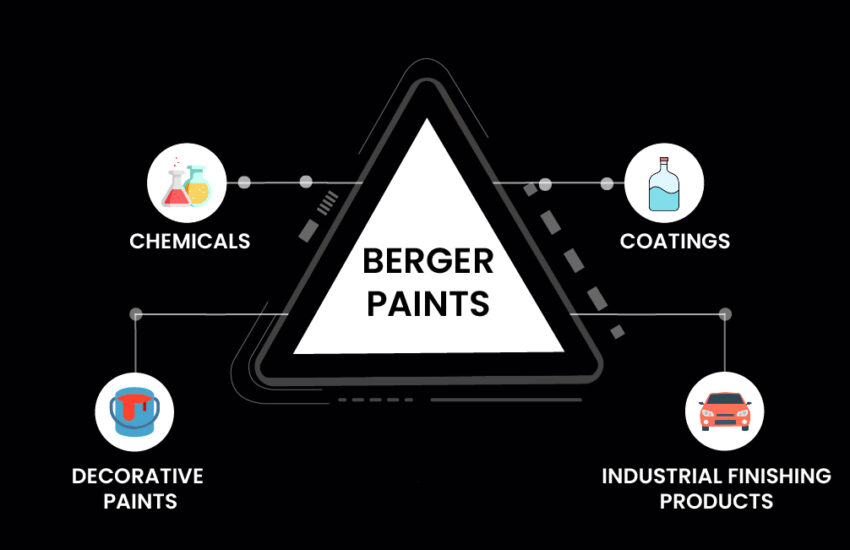
In India, the paint industry has been long characterized by the dominance of two significant players, Asian Paints and Berger
Continue reading
Have you ever noticed how everyday items have become more comfortable in recent years, with ergonomic designs that feel right
Continue reading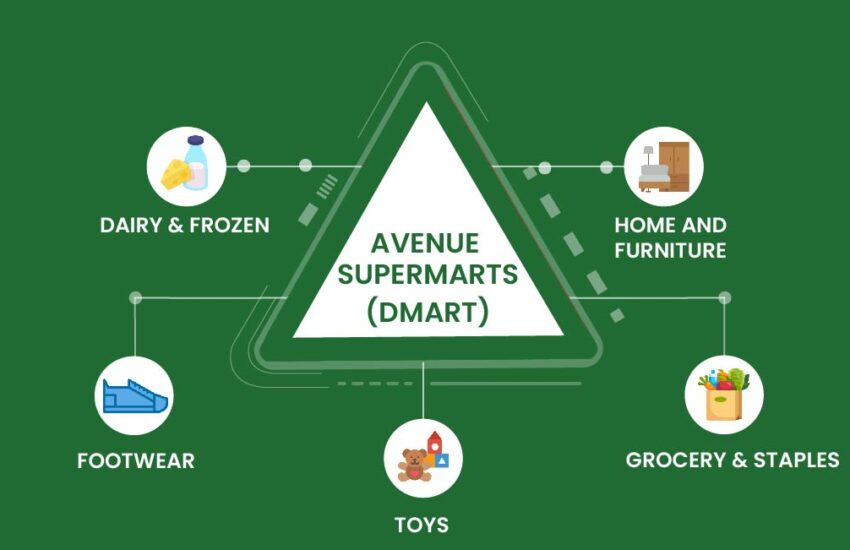
Introduction In a fiercely competitive market, where large and multinational retail chains are struggling to dominate and be profitable, Avenue
Continue reading
Introduction India is known as the “Pharmacy of the World” because of its ability to produce high-quality, low-cost generic and
Continue reading
Introduction Adani Group is India’s largest private Energy & Utility company, with a strong presence in Renewables, Power Generation, Transmission
Continue reading
Introduction In the last 10 years, Adani Group has emerged as a leading infrastructure and utility company in India, and
Continue reading
Introduction to HAL Hindustan Aeronautics Ltd. (HAL) is one of the oldest Indian companies specializing in aircraft and helicopter manufacturing
Continue reading
Introduction Over the past two decades, there has been a notable transformation in India’s power market structure. Initially, state electricity
Continue reading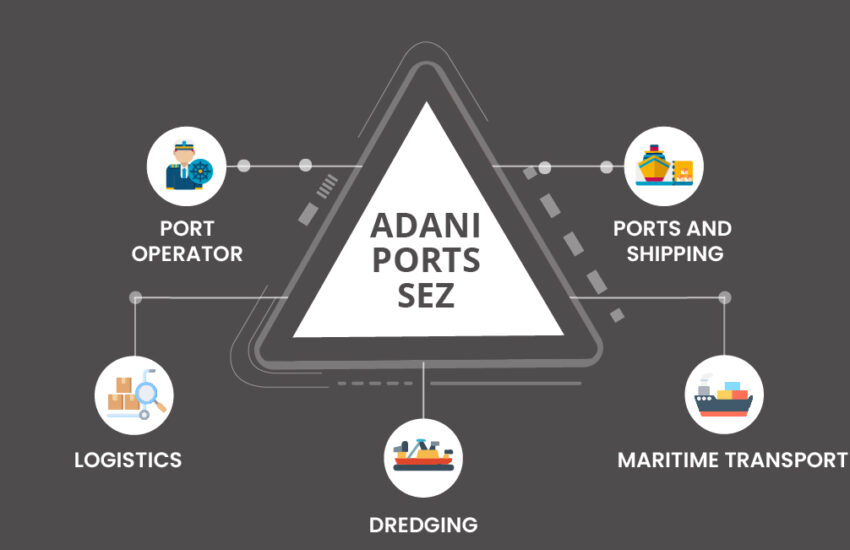
Summary Gautam Adani’s rise to become one of India’s most successful industrialists in recent years can be traced back to
Continue reading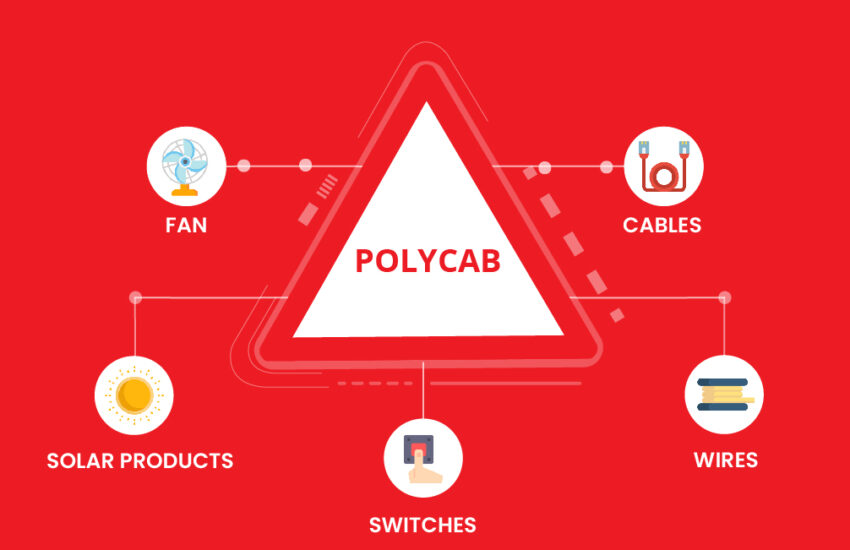
Summary The rise of Polycab India is inspiring by all means and shows the aspirational spirit of the Indians and
Continue reading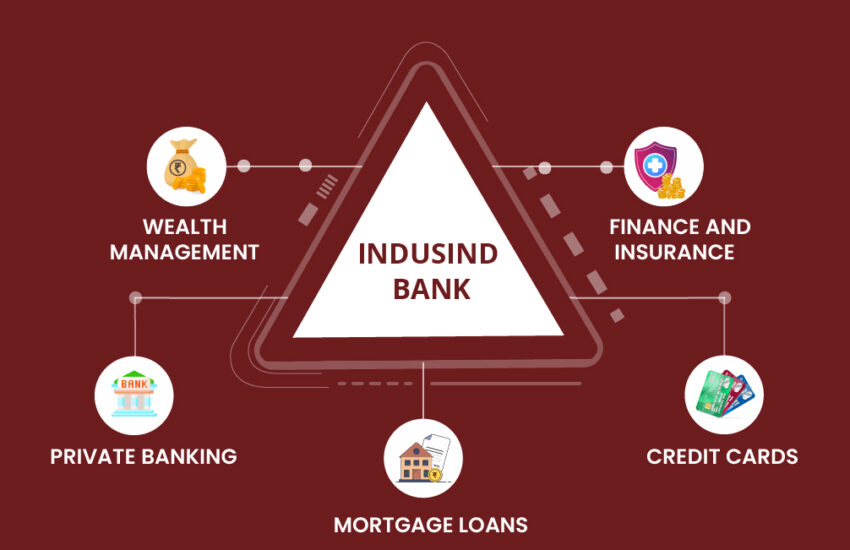
Summary IndusInd Bank started under the leadership of Mr. S.P. Hinduja to serve the NRI community. Today, IndusInd is the
Continue reading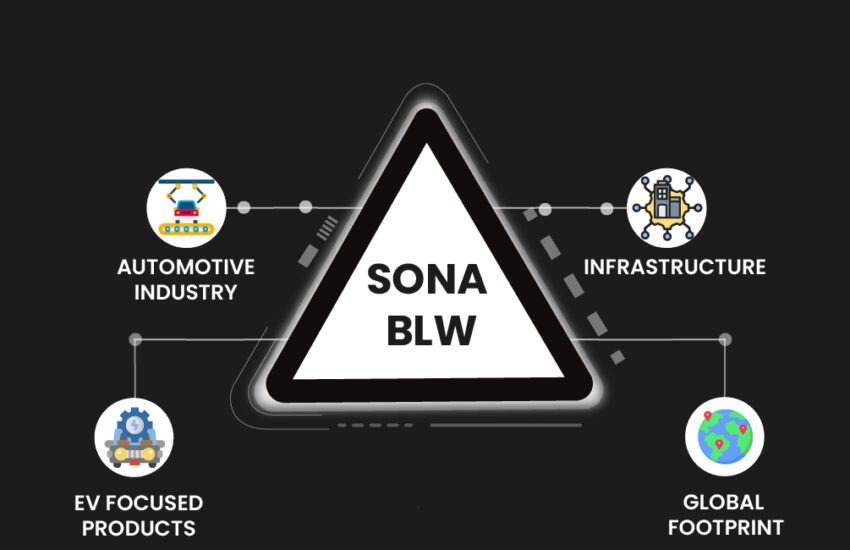
Introduction Sona BLW is a prominent Indian company with a global presence that manufactures differential gears, motors, and other components.
Continue reading
Introduction Since independence, Tata Steel and SAIL (The Steel Authority of India Limited) have played a key role in the
Continue reading
Introduction The Indian Pharmaceutical Industry is one of the world’s largest in terms of production by volume and value. It
Continue reading
Introduction Over the last decade, the share of credit disbursed to and by NBFCs in India has experienced significant growth,
Continue reading