Introduction
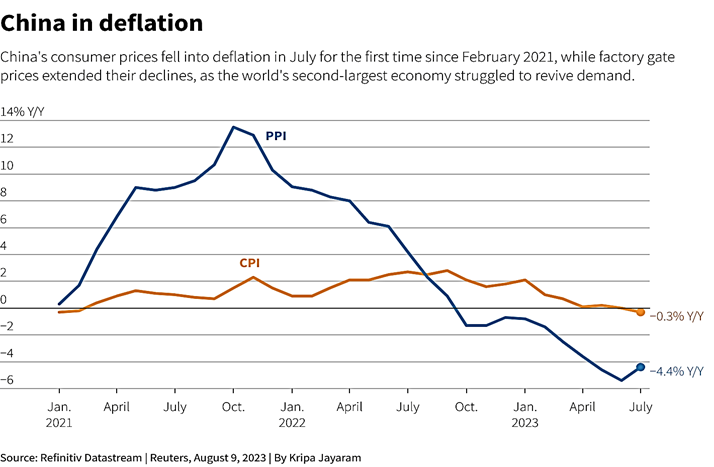
China is experiencing deflation. The recent decline of China’s Consumer Price Index (CPI) by 0.3% in July 2023 has sparked considerable attention and raised concerns about the state of the Chinese economy. This shift in trajectory becomes particularly evident when analyzing various critical indicators, as discussed in our recent Third Umpire video.
The overall economic landscape is less than promising, from sluggish property sales and construction activity to a deceleration in retail sales and alarming employment statistics. Adding to these woes is the significant drop in China’s exports, which have plummeted by around 14.5% compared to the previous year’s period.

A New Setback: China’s Consumer Sector in Deflation
China’s Consumer Price Index (CPI) is of utmost significance and has now taken center stage. The consumer sector in China has slipped into a state of deflation, underscoring the formidable challenges faced by the world’s second-largest economy in reigniting consumer demand.
Understanding Deflation
Deflation is characterized by a general reduction in the prices of goods and services, enabling consumers to purchase more with their available funds. However, this phenomenon can adversely affect businesses, as they are compelled to sell their products at lower prices, potentially reducing profits.
Key Takeaways
Unveiling the Setback: Consumer Prices and Producer Price Index
The announcement of deflation marks a significant setback for the Chinese economy, given that consumer prices experienced a decline in July for the first time in a span of two years. In parallel, the producer price index has also witnessed a decline of 4.4% in July, marking the tenth consecutive month of contraction. Notably, costs associated with essential categories such as food, transportation, and household goods have decreased during this period.
China’s Unique Position: A G20 Economy in Deflation
This disconcerting development places China in a unique position as the first G20 economy to report a year-on-year decline in consumer prices since Japan’s last negative CPI reading in August 2021. The stark difference in economic growth following the pandemic, domestically and globally, is notable.
Despite implementing various policies to boost the economy, the pace of revival within the nation has remained sluggish. Compared to many other economies grappling with inflation, China now finds itself entrenched in deflation.
Navigating Complexity: China’s Path Forward
China’s challenges are multifaceted and intricate, requiring careful navigation to address effectively. Managing these challenges and the potential for a turnaround in the country’s economic situation is a topic of great interest. Observers are keen to witness the strategies and measures that China will employ to steer its economy towards a more favorable trajectory.
In conclusion, China’s recent dip in the Consumer Price Index for July 2023 has ignited concerns about its economic trajectory. The emergence of deflation and its subsequent impact on various economic indicators highlight the complexity of China’s current situation. As the nation grapples with these challenges, it remains to be seen how China will chart its course forward and work to rejuvenate its economy.
FAQs
What is the Consumer Price Index (CPI)?
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is used to gauge changes in the average prices of a basket of goods and services households consume over time.
How does deflation affect businesses?
Deflation can reduce business profits, as they are compelled to lower their product prices. This can potentially impact their overall revenue and sustainability.
How has China’s economy been performing post-pandemic?
China’s economic growth post-pandemic has been lower than anticipated, both within the country and on the global stage, presenting unique challenges.
What sets China apart in terms of deflation among G20 economies?
China’s recent decline in consumer prices marks a distinctive position as the first G20 economy to report a year-on-year deflation since Japan in 2021.
What can we expect for the future of China’s economy?
The future of China’s economy is uncertain, but experts are keen to see how it will address its current challenges and strives for economic rejuvenation.
US Inflation Sees Moderate Rise in July 2023:Housing Costs Play a Key Role
Introduction
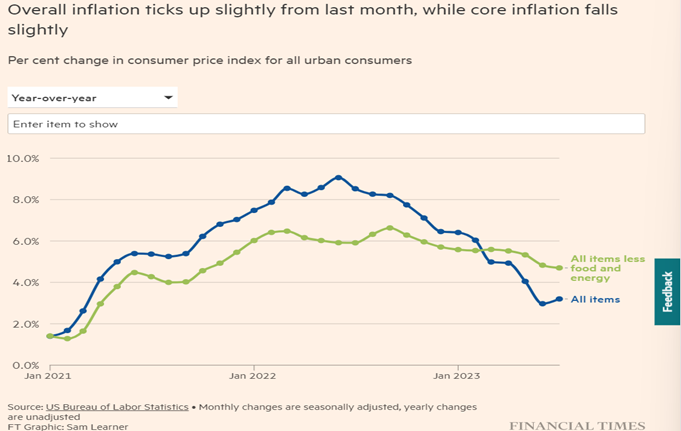
In a surprising turn of events, the United States witnessed a slower-than-expected rise in inflation during July 2023. After a year-long decline, inflation saw a modest increase, primarily driven by higher housing costs. The inflation rate for July edged up by 0.2 percentage points compared to the previous month, aligning with the uptick observed in June. Despite this upswing, the annual inflation rate reached 3.2% in July, a growth that fell short of initial predictions.
Understanding the Modest Uptick
The marginal increase in the annual inflation rate does not signal a substantial acceleration in inflationary pressures. Instead, it can be attributed to what economists refer to as “base effects,” influenced by a milder inflation reading recorded in July 2022. This incremental rise supports the notion that the Federal Reserve will likely maintain its interest rates at the upcoming September meeting.
Core Inflation: A More Stable Measure
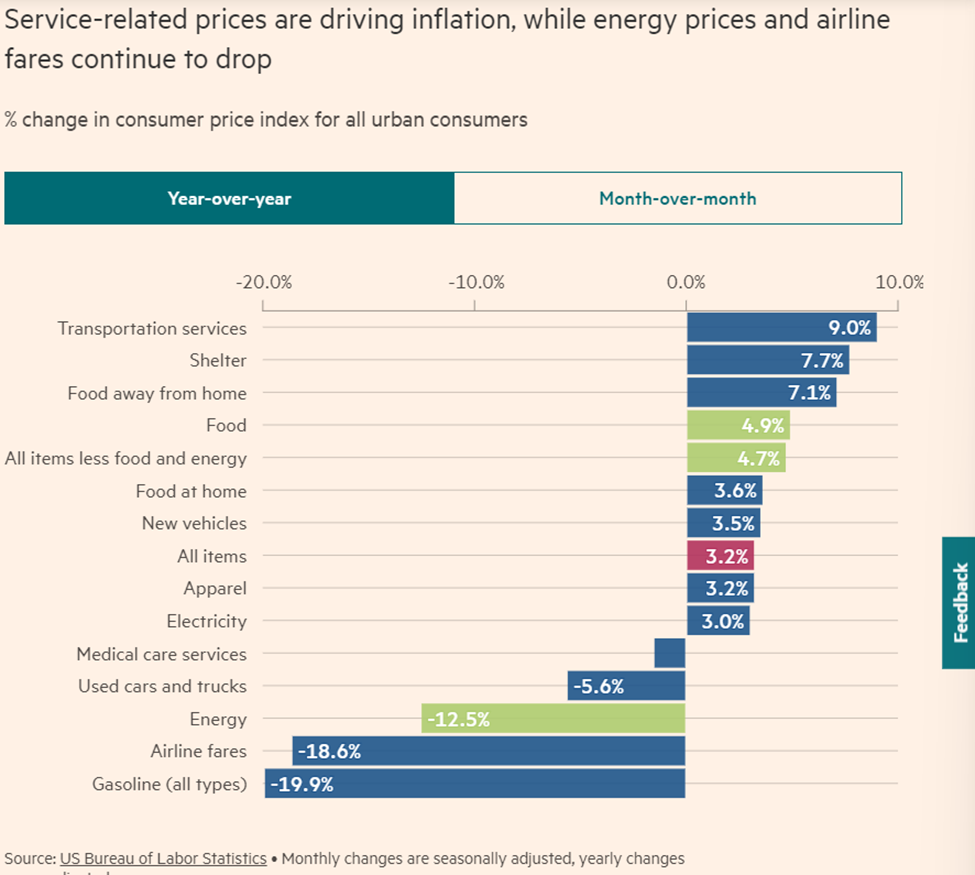
Core inflation emerges as a steadier metric when accounting for the volatile food and energy prices. In July, core inflation experienced a 0.2% increase, mirroring the growth rate of the preceding month. Notably, the year-on-year core inflation figure stood at 4.7%, marking a slower pace than June’s and representing the lowest level observed since October 2021.
Key Takeaways
- Meeting Analyst Expectations: The monthly inflation figures for headline and core inflation are closely aligned with the projections of analysts surveyed by Refinitiv. However, the annual figures fell slightly below the anticipated forecasts.
- Federal Reserve’s Response: Over the past 18 months, the Federal Reserve has executed a series of interest rate hikes, transitioning from near-zero rates to a notable range of 5.25-5.5%, the highest in 22 years.
- Inflation Trajectory: Following a peak of 9.1% in the previous summer, headline inflation has progressively approached the Fed’s 2% target. In contrast, core inflation has maintained a persistent elevation, placing pressure on the US central bank to uphold heightened interest rates for an extended duration.
- Impact on Fed’s Decision-Making: The latest report, particularly highlighting the improvement in core inflation, could potentially alleviate the pressure on the Federal Reserve to pursue further rate hikes within the remainder of the year. Last month, Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell emphasized that the central bank would take a meeting-by-meeting approach to determine future rate adjustments.
The July 2023 inflation report presents a nuanced perspective on the US economic landscape. While the rise in inflation is notable, its underlying causes and implications emphasize the intricate factors influencing the country’s monetary policy decisions. As the Federal Reserve continues to monitor these developments closely, the path forward will be determined by a delicate balance between economic indicators and the pursuit of stable economic growth.
FAQs
What caused the modest rise in US inflation in July 2023?
The increase in inflation during July was primarily driven by higher housing costs, contributing to a slight uptick in the overall inflation rate.
Why is the annual inflation rate lower than expected despite the monthly increase?
The annual inflation rate’s growth was influenced by what economists call “base effects,” which stem from a softer inflation reading in July 2022.
How does core inflation differ from headline inflation?
Core inflation excludes food and energy prices, providing a more stable measure of inflation trends.
What implications does the slower core inflation pace have on the US economy?
The lower core inflation rate may ease pressure on the Federal Reserve to implement further interest rate hikes in the near future.
Read more: How Long-term investing helps create life-changing wealth – TOI.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 0 / 5. Vote count: 0
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.

