Introduction
Recently, the Indian government’s efforts to divest its stake in various public enterprises have been challenged. Despite setting ambitious targets, the government has consistently fallen short of its disinvestment goals, creating a financial conundrum. This article delves into the ongoing struggle of the Indian government to achieve its disinvestment targets, exploring the reasons behind its underperformance and its implications for the nation’s fiscal landscape.
The Disinvestment Dilemma
A Stalled Move
The Indian government’s endeavor to sell its stake in IDBI Bank is a prime example of its disinvestment woes. Originally slated for completion by the end of the fiscal year, the sale has been pushed forward, and the target might not be met until the following March. This delay raises concerns due to the anticipated revenue of Rs 15,000 crore from the sale, which is crucial for reaching the overall disinvestment target of Rs 51,000 crore for the current financial year.
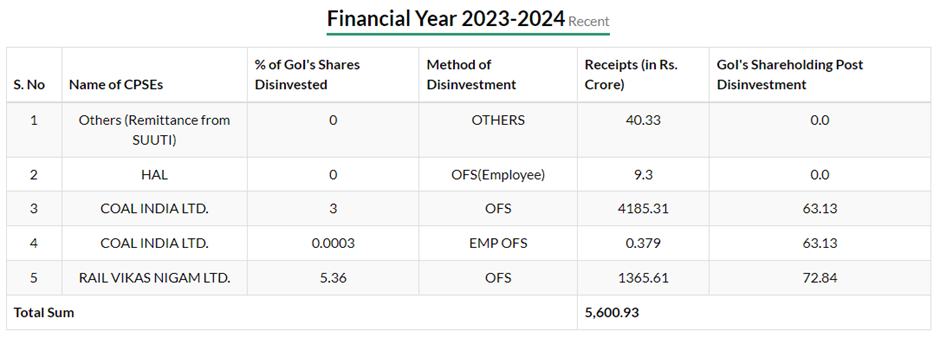
A Challenging Path
As of August 21, 2023, the Department of Investment and Public Asset Management (DIPAM) website revealed a stark reality – disinvestment receipts stood at a mere Rs 5,600.3 crore, a mere 11% of the government’s ambitious target. This glaring gap underscores the government’s uphill battle to achieve its goals.
Key Takeaways
A Persistent Pattern
The government’s struggle with disinvestment targets is not new. Over the years, they have consistently set high benchmarks but have repeatedly fallen short. The current situation reflects a more conservative approach, with the target for FY24 set at Rs 51,000 crore.
| Year | Budget Estimate | Actuals | Percentage of estimate realised |
| (in Rs crore) | (in Rs crore) | ||
| 2018-19 | 80,000 | 94,727 | 118% |
| 2019-20 | 1,05,000 | 50,304 | 48% |
| 2020-21 | 2,10,000 | Percentage of estimate realized | 16% |
| 2021-22 | 1,75,000 | 15,440 | 8.80% |
| 2022-23 | 50,000 | 31,107 | 62.21% |
| 2023-24 (Upto August 21, 2023) | 51,000 | 5,600 | 11% |
The Objective of Disinvestment
The core objective of disinvestment is to alleviate the government’s financial burden and generate funds for specific purposes. It serves as a safety net when traditional revenue sources prove insufficient. However, the government’s lackluster performance has raised questions about its effectiveness in reducing the fiscal deficit.
Relying on Alternatives
To mitigate the impact of disinvestment shortfalls, the government is banking on non-tax revenue sources, including dividends from the Reserve Bank of India and state-owned banks. This strategy is pivotal in maintaining the fiscal deficit target of 5.9% of the gross domestic product (GDP).
Investor Perspective
From an investor’s viewpoint, the outlook on the government’s ability to meet its divestment target is cautious. While achieving the target could boost confidence in the government’s economic strategy, failure to do so may not significantly affect fiscal calculations.
The Indian government’s struggle to meet disinvestment targets casts a shadow on its financial planning. Despite efforts to generate revenue through stake sales, persistent underperformance raises questions about the effectiveness of its strategies. As the nation navigates its fiscal landscape, balancing targets and execution remains challenging.
FAQs
Why is the Indian government struggling with disinvestment targets?
The government’s ambitious goals have consistently clashed with its ability to execute disinvestment plans effectively, leading to a pattern of underperformance.
What is the primary aim of disinvestment?
Disinvestment aims to ease the government’s financial burden and generate funds for specific needs, acting as a fallback when regular sources of revenue fall short.
How has the government compensated for disinvestment shortfalls?
To maintain its fiscal deficit target, the government relies on non-tax revenue streams, including dividends from the Reserve Bank of India and state-owned banks.
What implications does the government’s disinvestment struggle have on investors?
Investors are cautiously observing the government’s ability to meet its divestment target. Success could boost confidence, while failure may have a limited impact on fiscal calculations.
Why is the current disinvestment target more conservative?
Given the history of missed targets, the government has opted for a more prudent approach with a conservative target for FY24.
Strengthening US Dollar and Weakening Yuan Exert Pressure on Indian Rupee
The Indian Rupee Faces Downward Pressure
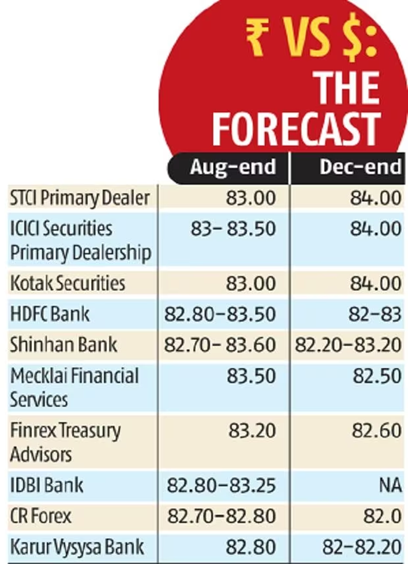
In recent developments, the Indian Rupee has been grappling with challenges, finding itself at an all-time low of 83.2 against the US dollar just last week. Unfortunately, the road ahead looks even more challenging as the currency braces for further decline due to the combined impact of a strengthening US dollar and a weakening Chinese yuan.
Market Sentiment in Numbers
An insightful poll conducted by Business Standard offers a snapshot of market sentiment. It reveals that 50% of participants braced for the rupee’s further weakening, foreseeing a touchpoint of 83.5. Conversely, the remaining 50% hold a more optimistic view, suggesting that the decline might reach its conclusion.
The Root Causes
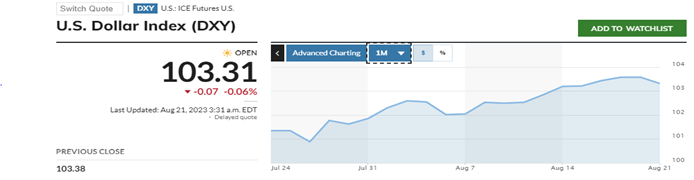
The primary driving force behind the rupee’s decline lies in the dollar index’s rise, which serves as a barometer of the US dollar’s strength. This surge in the index indicates the robustness of the US currency and adds significant pressure on other global currencies, including the Indian Rupee.
Additionally, the depreciating value of the Chinese yuan plays a role in this complex equation. The Chinese government has intentionally devalued the yuan as part of its strategy to revitalize its sluggish economy. This deliberate move by China further contributes to the challenging situation faced by the Indian Rupee.
Key Takeaways
Proactive Measures by the Reserve Bank of India
Recognizing the gravity of the situation, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has taken proactive measures to safeguard the stability of the Indian Rupee. These measures include strategic interventions through the sale of dollars to prevent the rupee from plummeting to historic lows.
The Resilience of the Indian Economy
The Indian economy, backed by substantial reserves of approximately $600 billion, stands on relatively solid ground. This robust reserve offers a cushion against the downward pressure on the rupee, positioning the Indian economy favorably amidst these turbulent currency dynamics.
Hope on the Horizon
Amidst the turbulence, there is a glimmer of hope on the horizon. While currently at its peak, the dollar index and rising US yields might eventually ease. This potential moderation could provide some much-needed relief to the struggling rupee.
Long-Term Considerations
Looking ahead, the Indian Rupee’s journey toward gaining recognition on the global stage hinges on multiple factors. The trajectory of export growth, the feasibility of achieving full capital account convertibility, and the sustained progress of the national economy are all critical determinants.
Prominence in the Global Currency Landscape
Despite the challenges, these factors could be pivotal in elevating the Indian Rupee’s prominence in the international currency landscape. As the Indian economy continues to evolve, the rupee has the potential to establish itself as a significant player on the global financial stage.
In conclusion, the Indian Rupee faces an intricate blend of factors as it navigates the impact of a strengthening US dollar and a weakening Chinese yuan. While challenges persist, strategic measures by the RBI and the resilience of the Indian economy offer a glimmer of hope for stability in these uncertain times.
FAQs
What factors are contributing to the decline of the Indian Rupee?
The Indian Rupee’s decline is influenced by the rise of the dollar index and the deliberate devaluation of the Chinese yuan, both of which exert pressure on global currencies.
How are experts predicting the rupee’s future trajectory?
A Business Standard poll shows that while 50% of participants anticipate further weakening, the other half believes the decline might be reaching its conclusion.
What measures has the RBI taken to address the rupee’s decline?
The Reserve Bank of India has proactively intervened through dollar sales to maintain the rupee’s stability and prevent it from hitting historic lows.
How does the Indian economy’s resilience factor into this situation?
With around $600 billion in reserves, the Indian economy is better positioned to withstand the downward pressure on the rupee, providing a cushion against currency fluctuations.
What long-term factors could contribute to the Indian Rupee’s global recognition?
The trajectory of export growth, capital account convertibility, and sustained economic progress will be crucial in determining the Indian Rupee’s prominence on the international currency stage.
Read more: How Long-term investing helps create life-changing wealth – TOI.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 0 / 5. Vote count: 0
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.

