Introduction
In recent years, India’s debt-to-GDP ratio has been a subject of much discussion and analysis. This critical economic indicator provides insights into the financial health of a nation. According to the latest estimates from the International Monetary Fund (IMF) in its Fiscal Monitor report, India’s debt-to-GDP ratio is projected to reach 82.3% in FY25, gradually declining to 80.5% in FY29.
The Impact of COVID-19
The COVID-19 pandemic, an unprecedented global event, had far-reaching effects on economies worldwide. India was no exception. The resultant decrease in government revenues and the surge in government spending led to a substantial increase in India’s public debt-to-GDP ratio, soaring from 75% in FY20 to 88.5% in FY21.
Fortunately, as both revenues and expenditures began to stabilize, there was a gradual decrease in India’s debt-to-GDP ratio to 81% in FY23. This offered a glimmer of hope amidst economic uncertainties.
IMF’s Revised Projections
However, the IMF’s latest projections paint a different picture. It anticipates a rise in the debt-to-GDP ratio over the next two fiscal years, in FY24 and FY25.
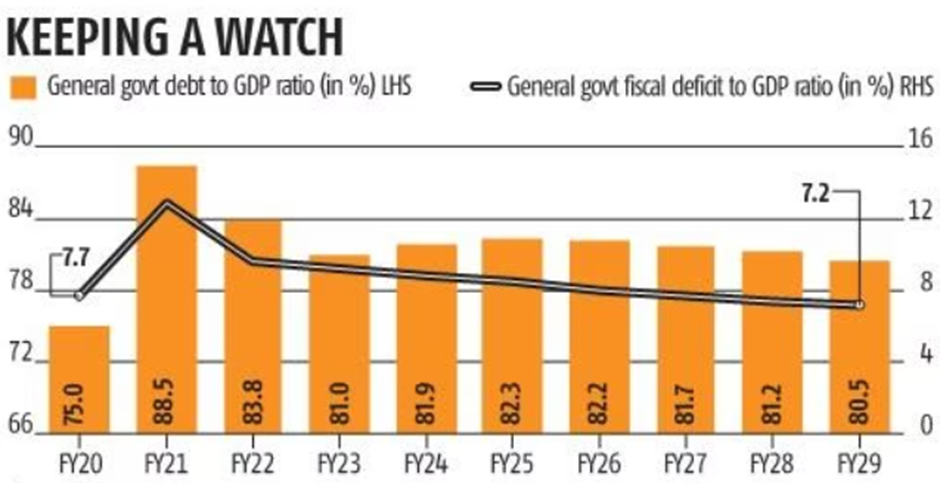
This revision is quite substantial compared to its earlier April projections, which indicated a four-year upward trajectory starting in FY24, culminating in a ratio of 83.8% in FY27.
Debt, when managed judiciously, can serve as a catalyst for economic growth. It provides the necessary funding for critical investments, ultimately stimulating economic development. Concerns arise only when debt intertwines with political instability and mismanagement.
It’s noteworthy that despite the seemingly high numbers, India maintains one of the lowest debt-to-GDP ratios among global economies. This underscores a commendable level of fiscal responsibility and prudence in managing its debt.
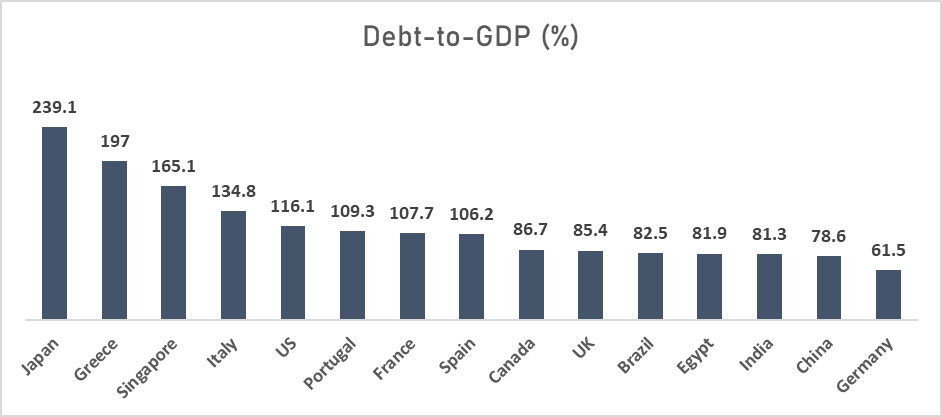
India’s external debt situation appears reasonably comfortable. Detailed information can be found in our third umpire videos for those seeking an in-depth exploration of India’s debt position.
Navigating the complexities of India’s debt-to-GDP ratio requires a nuanced understanding of economic realities. The IMF’s revised projections signal a need for careful fiscal planning and management in the years ahead. However, India’s comparative advantage in maintaining a relatively low ratio showcases its commitment to economic stability and growth.
FAQs
What is a debt-to-GDP ratio?
The debt-to-GDP ratio is a financial indicator that compares a country's total debt to its gross domestic product (GDP). It provides insights into a nation's ability to manage its debt in relation to its economic output.
How does India's debt-to-GDP ratio compare globally?
India maintains one of the lowest debt-to-GDP ratios compared to other major economies, indicating a responsible approach to fiscal management.
What factors contributed to the surge in India's debt-to-GDP ratio in FY21?
The COVID-19 pandemic led to a decrease in government revenues and an increase in government spending, which in turn caused a significant rise in India's debt-to-GDP ratio.
How can India work towards reducing its debt-to-GDP ratio in the long term?
Long-term reduction of the debt-to-GDP ratio requires a combination of prudent fiscal policies, effective revenue generation, and careful management of government expenditures.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 0 / 5. Vote count: 0
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.

