Introduction
Amid a worldwide economic deceleration, India’s economic canvas has encountered a disquieting trend in the first quarter of the year, with a notable dip in net Foreign Direct Investment (FDI).
Insights for the Informed Investor
Foreign direct investment within the nation significantly declined, plummeting to 4.99 billion dollars in the first quarter, marking a substantial contrast from the $13.92 billion dollars recorded in the same period the previous year.
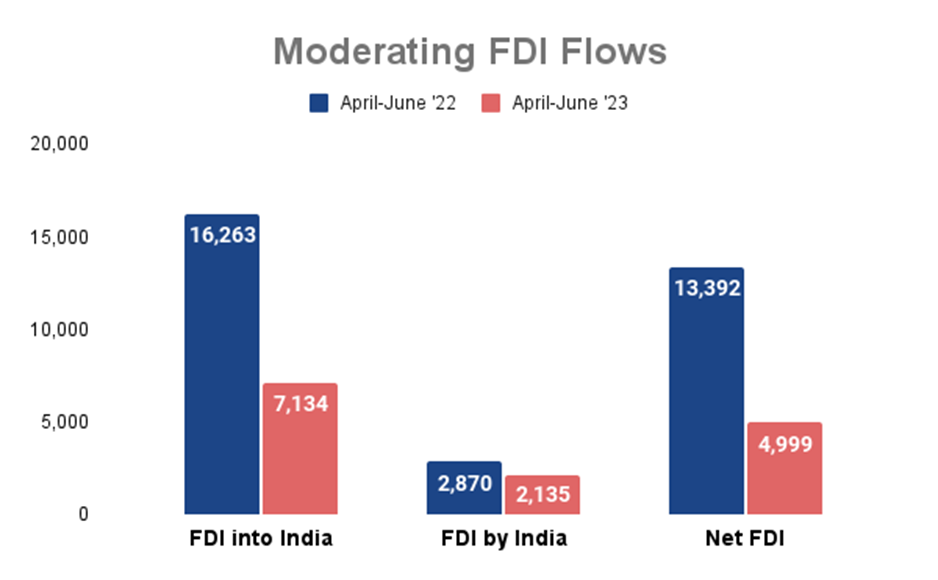
Among the sectors, manufacturing, financial services, business services, computer services, electricity, and other energy segments collectively accounted for over two-thirds of the new equity inflows in this interval.
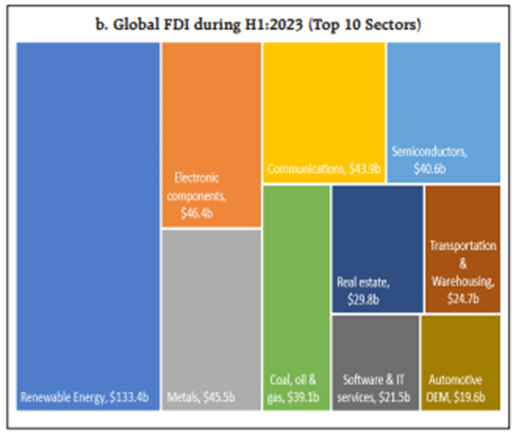
A more granular examination of India’s performance in the year’s initial half uncovers that the renewable energy sector took the lead in attracting FDI, closely pursued by electric components and metals. Furthermore, communication, semiconductors, oil and gas, among others, secured positions in the top 10 sectors that garnered FDI. Noteworthy contributors to this FDI influx included countries such as Singapore, the Netherlands, Japan, the US, and Mauritius.
Key Takeaways
Interpreting the Trends
The slump in FDI inflows can be attributed to a combination of factors, including the looming global economic downturn and surges in inflation and interest rates. According to a report from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), the moderation in gross inward FDI, alongside an upswing in the repatriation of investments, has collectively led to this decline. While India remains positioned advantageously, the emergence of global headwinds poses a potential impediment to the nation’s FDI inflows in the immediate future.
Despite these challenges, India’s trajectory appears promising. The country stands at the intersection of opportunities, fortified by the ongoing robust Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme and a pronounced push in capital expenditure. These domestic initiatives are poised to counterbalance the obstacles posed by global economic dynamics, reaffirming India’s commitment to sustaining FDI inflows and propelling its economic growth.
As India treads through these dynamic economic times, the nation’s resilience and proactive measures are anticipated to play a pivotal role in shaping its FDI trajectory, influencing domestic and global stakeholders.
FAQs
What is the recent trend in India’s FDI inflows?
India’s FDI landscape witnessed a substantial decline, with net Foreign Direct Investment falling to $4.99 billion in the first quarter, compared to $13.92 billion in the same period of the previous year.
Which sectors attracted the majority of fresh equity flows during this period?
Manufacturing, financial services, business services, computer services, electricity, and other energy sectors collectively accounted for more than two-thirds of the new equity inflows during this period.
What factors contributed to the decline in FDI inflows?
The decline in FDI inflows can be attributed to the global economic slowdown and high inflation and interest rates. Additionally, the Reserve Bank of India’s report cites moderation in gross inward FDI and increased repatriation of investments as factors behind the decline.
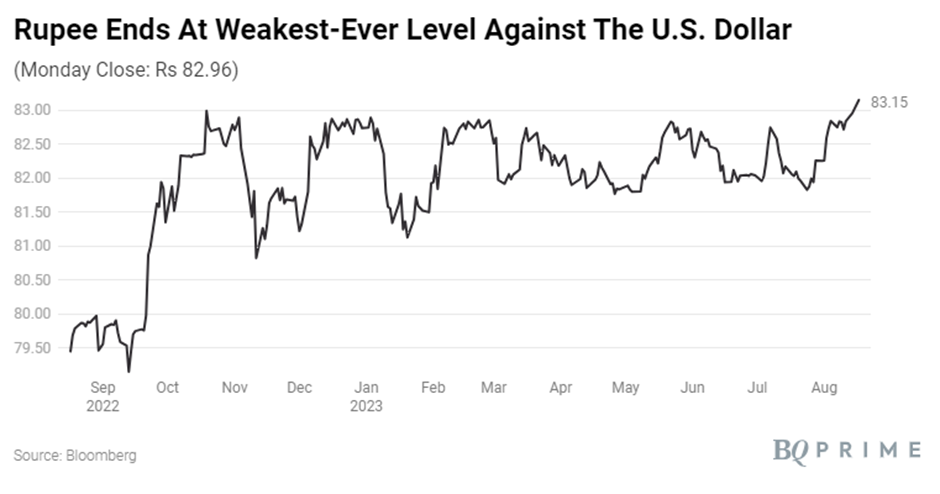
Rupee’s Dip Unveiled: Unraveling Factors Behind the Decline
In a swift turn of events on Thursday, the rupee experienced a 20 paise plunge, reaching an unprecedented record closing low of 83.15 against the US dollar. Several factors seem to have contributed to this scenario, including the surge in US bond yields and a decline in the Chinese yuan.
In-depth Analysis for the Curious Observer
The past week witnessed a pronounced ascendancy of the dollar. This sudden surge was prompted by cues from the US Federal Reserve, suggesting the possibility of additional rate hikes as a measure to curb inflation. Subsequently, US bond yields surged, bolstering the dollar’s strength. The rationale here lies in higher yields rendering US securities more alluring to global investors, enhancing the dollar’s appeal.
Enter the Chinese yuan, a pivotal player in this narrative. The yuan’s depreciation often stems from apprehensions concerning China’s economic stability. This phenomenon can shift investor sentiment, driving them towards safer assets like the US dollar. Consequently, emerging market currencies, including the Indian rupee, frequently experience weakening trends.
Key Takeaways
While the present rupee depreciation closely aligns with the dominant performance of the dollar index, it’s crucial to delve into India’s ongoing endeavors to bolster the utilization of the rupee in international trade. This movement towards de-dollarization and currency diversification holds significance. A notable instance this week involved a substantial announcement by the Indian government. Indian Oil Corp., a leading petroleum refiner, utilized the local rupee to procure one million barrels of oil from the Abu Dhabi National Oil Company, effectively bypassing the US dollar.
However, emancipating from the stronghold of the US dollar is a complex undertaking. The dollar has long retained its status as a safe haven and is widely accepted globally. Detaching from its dominance necessitates meticulous strategy and concerted efforts.
The long-term prospects for the rupee’s heightened global recognition rest on a multifaceted foundation. These factors encompass the trajectory of export growth, the feasibility of achieving capital account convertibility, and the continuous evolution of our economy. While challenges persist, these elements can potentially carve out an enhanced position for the Indian rupee on the global currency map.
FAQs
What caused the recent decline in the Indian rupee’s value?
The rupee’s decline can be attributed to a combination of factors, including the rise in US bond yields and a fall in the Chinese yuan.
How did the surge in US bond yields impact the dollar’s strength?
Higher yields on US bonds made US securities more attractive to global investors, increasing the strength of the US dollar.
What role does the depreciation of the Chinese yuan play in the scenario?
The depreciation of the Chinese yuan often triggers concerns about China’s economic well-being, leading investors to opt for safer assets like the US dollar. This trend weakens currencies across emerging markets, including the Indian rupee.
Read more: How Long-term investing helps create life-changing wealth – TOI.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 3 / 5. Vote count: 1
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.

