The stock market has endless opportunities for those who know how to churn profits from it. Besides investing the traditional way, some savvy investors also make good money by using smart tactics. One such common strategy is arbitrage.
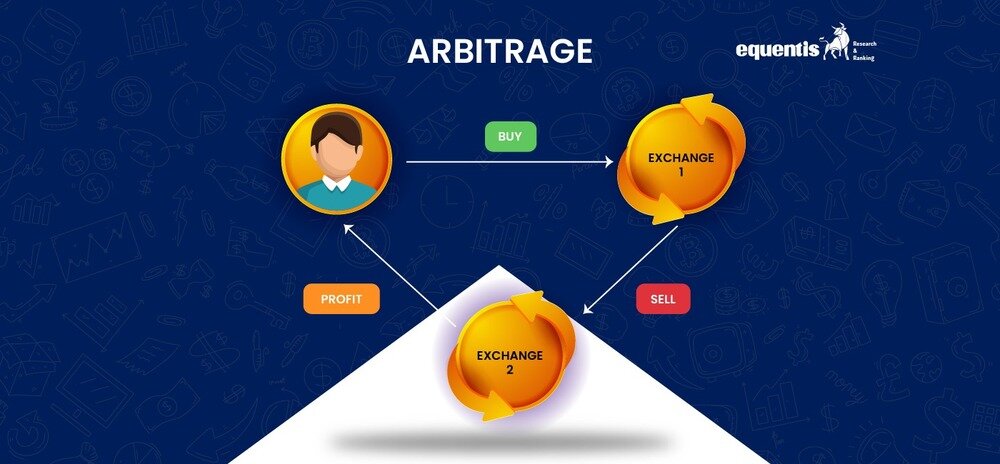
Arbitrage is an age-old investment strategy that allows you to take advantage of the price differences in different stock markets. It is similar to buying a product from a cheaper market and then selling it in a market that offers a higher price.
Understanding this strategy can help you maximize your gains and set a firm foot in the stock market.
In this blog, we will explain everything you need to know about this stock market concept, from arbitrage fund meaning and how it works to how to get started.
Arbitrage Meaning: What Is Arbitrage Fund Meaning?
Arbitrage refers to the process of generating profit from trading investment instruments such as securities, currencies, and commodities in two different markets.
In essence, the arbitrageurs gain their profit margin from the different prices of the same product in two different stock exchanges.
The concept of Arbitrage is based on the market efficiency theory. According to this theory, there must be no scope for arbitrage if the market is completely efficient. In simple words, the same or equivalent assets/securities must have the same price across all the markets and regions.
.
How Does Arbitrage Work?
Understanding arbitrage’s meaning is not enough to conclude whether it is a good strategy. It is also important to understand how this concept actually works.
As mentioned above, Arbitrage is a technique for buying and selling the same shares in two different markets simultaneously. However, it is not as easy as it sounds. It requires experience and efficient portfolio management to select and manage such lucrative opportunities.
An Example Illustration of Arbitrage
Let’s understand this concept with the help of an example.
Suppose a stock is listed on both NSE as well as BSE. Due to stock market fluctuations and other factors, the price of stock on NSE is ₹100, while it is ₹103 on BSE.
To gain a profit of ₹3 per share, you purchase 10 shares from NSE at ₹1,000 and sell them on BSE at ₹1,030. You can continue buying/selling this stock until the prices across both markets have matched.
Opportunities of Arbitrage
Traders or Arbitrageurs can make profits in two ways. As discussed, the first method involves buying at a low price and selling at a higher price, and the second method is just the opposite.
You sell a security (or other trading instrument) at a higher price at one stock exchange or market and buy it at a lower price at the other market.
This way, you can keep earning profits until the price of the instruments is the same in both markets. It is important to note that investing in shares using this strategy is done carefully in real-time.
There are some popular arbitrage opportunities used by most traders:
- Security: It involves buying and selling shares, stocks, equities, bonds, and other instruments in two different stock or share markets.
- Currency: It involves acquiring a currency at nominal value and selling it at a higher value.
- Commodity: It usually involves buying goods at cheaper prices from one country and selling them at a higher price in other countries.
Theory of Arbitrage: Beware of Transaction Costs
Arbitrage may sound exciting, but you must take the transaction cost into account before implementing this strategy.
If the transaction cost is very high, it will neutralize your profits. Taking the example mentioned in the above section, if the cost of trading per share is ₹1.5, your profit will decrease by ₹15 from ₹30.
Is Arbitrage Legal?
Yes. Arbitrage is a legal strategy used by many traders worldwide. Its main reason for popularity is the liquidity it provides.
Besides, it also helps in identifying the weaknesses of the markets and promoting price convergence.
Are Arbitrage Funds Low-Risk?
Arbitrage funds, as the name suggests, are mutual funds that aim to generate profitable returns from the price differences in two separate market segments by trading the assets/securities simultaneously.
Arbitrage funds are generally perceived as low-risk options because they allow traders to take advantage of market price differences. However, they are not completely risk-free.
Timing is crucial in executing arbitrage funds. Any delay or trading mistake can negate your gains.
In addition, higher transaction costs, liquidity problems, market fluctuations, and sudden regulations can also add to the risky nature of arbitrage funds.
The Bottom Line
Arbitrage is an action of profiting from price variations in different markets. As discussed in the blog, it involves buying shares at a low price from a market or stock exchange and selling them at a better price on a different exchange.
Although it can be profitable to some extent, it also helps in highlighting the flaws of the markets thereby limiting your profitability.
For these reasons, the concept of arbitrage should be implemented carefully after reading stock charts and performing market research. If you have limited experience or stock market exposure, seek guidance from a financial advisory before getting started.
Frequently Asked Questions
Who is an arbitrageur?
An arbitrageur is a person or entity that performs arbitrage by exploiting the price differences of an investment instrument or commodity in two different markets.
Is arbitrage the same as hedging?
No. Arbitrage and hedging are two completely different concepts. Arbitrage refers to a method of generating profit through price discrepancies in the markets. On the other hand, hedging is a method of bypassing investment risks by counterbalancing financial transactions.
What is spatial arbitrage?
Spatial arbitrage is a method of benefitting from the price differences of the same commodity or security in two different regions or locations. In simple terms, it means buying an asset from a physical location (such as a country) at a lower price and selling it at a location that offers a higher price.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 0 / 5. Vote count: 0
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
I’m Archana R. Chettiar, an experienced content creator with
an affinity for writing on personal finance and other financial content. I
love to write on equity investing, retirement, managing money, and more.
-
Archana Chettiarhttps://www.equentis.com/blog/author/archana/
-
Archana Chettiarhttps://www.equentis.com/blog/author/archana/
-
Archana Chettiarhttps://www.equentis.com/blog/author/archana/
-
Archana Chettiarhttps://www.equentis.com/blog/author/archana/