Economy – Blog Category
This section offers content on things happening in the country. Any news update on India, its GDP, plans and levels globally will be included in this section.
Amid the rising interest rates, chatter around the impending recession in 2023 is slowly gaining strength. And, with recent bank […]
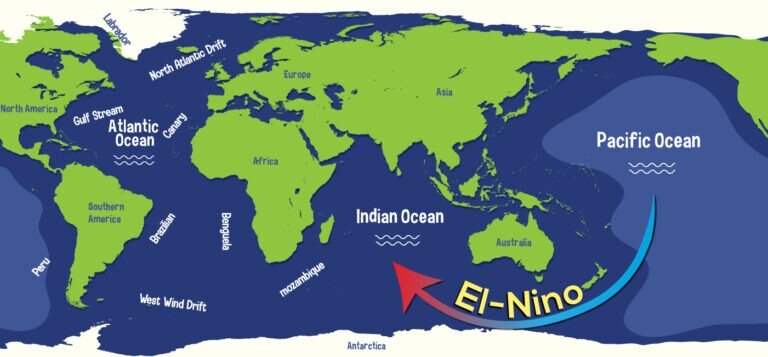
This update from the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) may worry you and affect the choice of food on your plate […]
UPI Payment for International Travellers RBI extended UPI payments for international travellers facilitating local payments at G20 meeting venues and […]
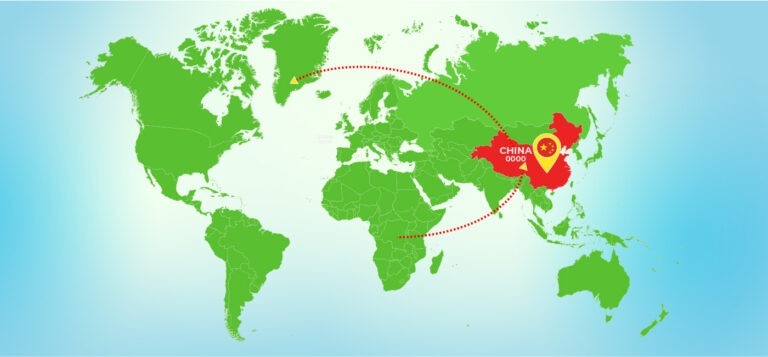
China borders reopening in 2023 marked a highly anticipated event for global trade and investments after extended travel restrictions due […]
The Indian Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) published its fourth draft of the proposed privacy law, renamed the […]
The Economic Survey is an annual report published by the Government of India that reviews the country’s financial developments over […]
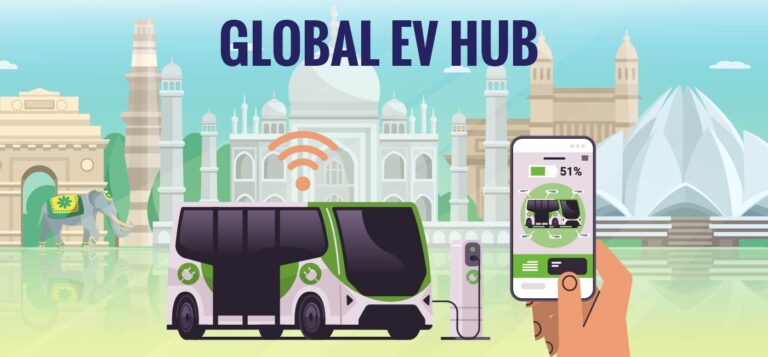
The EV market in India is expected to reach $47 billion by 2026, reducing our reliance on fossil fuels significantly over time. […]
Overview of the Steel Industry Steel production emits over 3 billion metric tonnes of CO2 annually, making it the industrial […]
Indian handicrafts are a vital part of the country’s cultural and economic fabric, with a long history dating back to […]
UK Prime Minister Rishi Sunak reaffirmed UK’s commitment to a free trade agreement with India, stating that it would be […]
Frequently asked questions
Get answers to the most pertinent questions on your mind now.
What is an Investment Advisory Firm?
An investment advisory firm is a company that helps investors make decisions about buying and selling securities (like stocks) in exchange for a fee. They can advise clients directly or provide advisory reports and other publications about specific securities, such as high growth stock recommendations. Some firms use both methods, like Research & Ranking, India’s leading stock advisory company, specializing in smart investments and long-term stocks since 2015.
Do we have SEBI registration as an Investment Advisory?
An investment advisory firm is a company that helps investors make decisions about buying and selling securities (like stocks) in exchange for a fee. They can advise clients directly or provide advisory reports and other publications about specific securities, such as high growth stock recommendations. Some firms use both methods, like Research & Ranking, India’s leading stock advisory company, specializing in smart investments and long-term stocks since 2015.
Why choose a SEBI Registered Investment Advisor?
An investment advisory firm is a company that helps investors make decisions about buying and selling securities (like stocks) in exchange for a fee. They can advise clients directly or provide advisory reports and other publications about specific securities, such as high growth stock recommendations. Some firms use both methods, like Research & Ranking, India’s leading stock advisory company, specializing in smart investments and long-term stocks since 2015.
What is the Role of an Investment/Stock Market Advisory Firm in India?
An investment advisory firm is a company that helps investors make decisions about buying and selling securities (like stocks) in exchange for a fee. They can advise clients directly or provide advisory reports and other publications about specific securities, such as high growth stock recommendations. Some firms use both methods, like Research & Ranking, India’s leading stock advisory company, specializing in smart investments and long-term stocks since 2015.