The stock market, often looked upon as a complex concept, can be understood with the right guidance. Questions like “What is a stock?” and “How do I start investing?” are common among beginners. But understanding the fundamentals of the stock market is not just for aspiring investors; it’s a valuable skill for anyone seeking financial literacy.
By grasping the basics of how the stock market works and the steps to navigate it, you can gain insights into wealth creation and make informed financial decisions. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting your journey, exploring the stock market for beginners can open doors to a world of financial opportunities. Here are 10 things to remember for stock market beginners.
Share market for beginners often feels like a daunting topic, but in reality, with the right knowledge and tools, anyone can learn to invest wisely. Understanding the share market is not just about buying and selling stocks, it’s about gaining financial literacy, making informed decisions, and preparing for a financially secure future.In this guide, we break down the stock market basics for beginners and explore everything from how to get started to advanced topics that build confidence in investing.
What is the Stock Market?
Imagine a marketplace, but instead of selling fruits and vegetables, it sells pieces of companies. This marketplace is the stock market. When a company wants to raise money to grow its business, it can sell shares of itself. These shares are like tiny pieces of ownership in the company.
The stock market is a platform where investors buy and sell shares of publicly listed companies. When you buy a share, you purchase a small part of the company and hence become a part-owner of that company. If the company does well, the value of your shares may increase. Conversely, if the company struggles, the value may decrease.
Stocks and shares are often used interchangeably, but shares can refer to ownership in different entities, while stocks usually mean ownership in a company.
Why Understanding the Share Market is Crucial for Beginners
Financial literacy is becoming increasingly important. This guide to share market for beginners is a starting point for understanding how to grow wealth, manage risks, and achieve long-term financial goals. By learning how to invest in the stock market, you gain the power to:
- Generate passive income
- Beat inflation over time
- Build wealth through compounding returns
- Diversify your investment portfolio
Overview of Stock Market Basics
How does the stock market work?
The stock market can be regarded as a digital auction house for companies. In the past, people physically gathered on trading floors to buy and sell shares. Today, it’s mostly done electronically.
Here’s a simplified breakdown:
- Listing: A company first needs to list its shares on a stock exchange. This involves meeting certain regulatory requirements.
- Trading: Once listed, the company’s shares can be bought and sold by investors through brokers.
- Price Fluctuation: The price of a share is determined by supply and demand. If more people want to buy a particular stock, its price rises. If more people want to sell, the price falls.
Key Components:
- Stock Exchanges: Platforms like the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and National Stock Exchange (NSE) allow users to buy and sell stocks in an authorised and regulated environment.
- Types of Stocks: Common stocks (voting rights, dividends) vs. Preferred (priority in dividends but no voting rights).
- Market Participants:
- Investors: Long-term participants who aim for steady returns
- Traders: Short-term participants seeking quick profits
- Brokers: Intermediaries who facilitate buy/sell transactions
Key Terms and Concepts in the Stock Market
- Stocks, Shares, and Securities: Ownership units in companies
- Market Orders: Execute at the current market price
- Limit Orders: Execute at a specified price or better
- Stop-Loss Orders: Sell automatically at a trigger price to limit loss
- Indices (Sensex, Nifty): Indicators of overall market performance
Market Capitalization: Total value of a company’s shares in the market
Why Do People Invest in the Stock Market?
Investing in the stock market offers a pathway to grow wealth over time. Stocks historically outperform other asset classes like bonds or savings accounts in the long term.
NOW READ: Mutual Funds vs Equity | Gold vs Stocks
– Wealth Creation: A disciplined approach to stock investing has helped individuals grow their investments significantly.
– Compounding: Reinvesting dividends over time can lead to exponential growth.
– Passive Income: Dividend-paying stocks can generate steady returns without active involvement.
As a Beginner, When Should You Invest in Stocks?
Timing your entry into the stock market is tricky. For stock market beginners, it’s best to avoid trying to time the market perfectly. Instead, focus on long-term goals and invest regularly through methods like Systematic Investment Plans (SIPs). This helps mitigate risks and ensures you’re not overly exposed to market volatility.
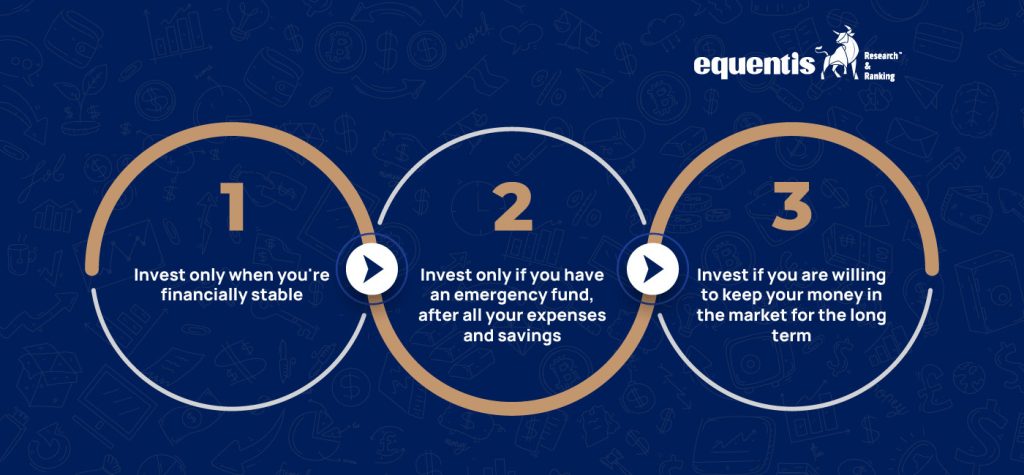
If you’re a beginner in the stock market, invest only if you meet these 3 conditions –
- Invest only when you’re financially stable
- Invest only if you have an emergency fund, after all your expenses and savings
- Invest if you are willing to keep your money in the market for the long term
Share market advisory services can help you understand the best times to enter the market based on current conditions.
Stock Market Guide for Beginners
Stock investing involves buying and selling shares of publicly-traded companies. When you buy a stock, you become a part-owner of the company. The stock market is a platform where these shares are traded.
Stock Market Terms & Concepts
- Market Capitalization: The total value of a company’s outstanding shares.
- IPO (Initial Public Offering): The first sale of a company’s stock to the public.
- Bull Market: A market condition where prices are rising.
- Bear Market: A market condition where prices are falling.
- Volatility: The degree of price fluctuation in a stock or the market.
- Liquidity: The ease with which a stock can be bought or sold.
- Stock: A share of ownership in a company.
- Share Market: A marketplace where stocks are bought and sold.
- Stock Exchange: An organized marketplace for buying and selling stocks.
- Broker: An intermediary who facilitates buying and selling of stocks.
- Dividend: A portion of a company’s profits paid to shareholders.
- P/E Ratio (Price-to-Earnings Ratio): Measures the price of a stock relative to its earnings per share.
- Dividend Yield: The annual dividend per share divided by the stock price.
- Buy and Hold: A long-term investment strategy involving buying and holding stocks for an extended period.
- Day Trading: Buying and selling stocks within the same trading day.
- Swing Trading: Holding stocks for a few days or weeks to profit from short-term price swings
- Diversification: Spreading investments across different stocks and asset classes to reduce risk.
- Risk Tolerance: An individual’s capacity to withstand market fluctuations.
- Stop-Loss Order: An order to sell a stock at a specific price to limit potential losses.
Investment Strategies in the Stock Market
- Buy and Hold: A long-term strategy involving buying and holding stocks for an extended period.
- Day Trading: Buying and selling stocks within the same trading day.
- Swing Trading: Holding stocks for a few days or weeks to profit from short-term price swings.
Fundamental and Technical Analysis Basics
To succeed in the stock market, understanding these analysis techniques is essential:
Focuses on evaluating a company’s health using metrics like:
– P/E Ratio: Price-to-Earnings ratio shows valuation.
– Earnings Reports: Quarterly data on revenue and profits.
Technical Analysis:
Relies on historical data and charts to predict trends using tools like:
– Moving averages.
– Support and resistance levels.
– Resources: Our stocks screener provides data and analysis tools for beginners.
How to Invest in Stock Market if You are a Beginner
Starting in the stock market can feel overwhelming for beginners, but with the right steps, it becomes easier. Here is a list of do’s and don’ts they need to follow.
How to Start Investing in the Share Market
Step 1: Open a Demat and Trading Account
Opening a demat account is the first step to start investing. A Demat account stores your shares electronically. A trading account facilitates transactions. Many platforms offer integrated accounts.
Step 2: Understand Your Risk Profile
Understanding your tolerance for loss should be the next step.
Step 3: Research and Choose Stocks
Use financial news, analyst reports, and company fundamentals (P/E ratio, profit margins, sector growth) to evaluate potential investments.
Stock Market Investment Strategies for Beginners
- Long-Term Investing: Minimizes risks, benefits from compounding
- Short-Term Trading: Suitable for experienced investors only
- SIP (Systematic Investment Plan)/SEP (Systematic Equity Plan): Invest a fixed amount regularly
- Mutual Funds: Managed portfolios, ideal for beginners.
How to Read Stock Market Data and Charts
Reading stock charts is a fundamental skill for any investor. These charts offer visual insights into the price behavior of stocks, helping you make informed decisions.
- Candlestick Charts: These are graphical representations of price movements for a specific time period. Each candlestick shows four data points: the opening price, closing price, high, and low. A green (or hollow) candlestick usually indicates that the closing price was higher than the opening price (bullish), while a red (or filled) one shows the opposite (bearish).
- Indicators:
- Moving Averages: This indicator smooths out price data to identify the direction of a trend. A simple moving average (SMA) takes the average of closing prices over a set time period (e.g., 50-day SMA), while an exponential moving average (EMA) gives more weight to recent prices. These help traders determine support/resistance levels and identify entry or exit points.
- RSI (Relative Strength Index): RSI measures the speed and change of price movements. It ranges from 0 to 100. An RSI above 70 indicates that a stock may be overbought and due for a correction, while below 30 suggests it may be oversold and could rebound.
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): This momentum indicator shows the relationship between two moving averages, typically the 12-day and 26-day EMAs. It consists of the MACD line, the signal line (usually a 9-day EMA of the MACD), and a histogram.
Types of Stock Market Orders
- Market Orders: Buy/sell at current price
- Limit Orders: Set specific buy/sell price
- Stop-Loss Orders: Protect from major losses by auto-selling
Common Stock Market Mistakes to Avoid
- Investing Without Research: Failing to study the companies or the overall market before investing often leads to poor decisions. Beginners should take time to understand a company’s financial health, industry trends, and future outlook before putting their money in.
- Overtrading: Engaging in too many trades in a short period can increase brokerage fees and taxes, and may also lead to emotional decision-making. A disciplined approach with fewer, well-researched trades is usually more effective.
- Emotional Investing: Letting emotions like fear, greed, or excitement dictate investment decisions can be detrimental.
- Lack of Diversification: Putting all your money into a single stock or sector increases vulnerability. If that particular investment performs poorly, it can wipe out a significant portion of your capital.
Stock Market Risks and Rewards for Beginners
- Potential Returns: Investing in the equity markets has historically provided superior long-term returns compared to more traditional asset classes such as fixed deposits or savings accounts.
- Market Volatility: Volatility refers to the rapid and unpredictable movement in stock prices. These fluctuations can be triggered by a range of factors including economic data, company earnings reports, geopolitical events, interest rate changes, and investor sentiment.
- Risk Management: Investing in equity allows one to diversify the investment, minimizing the overall risk and maximizing returns.
How to Monitor Your Stock Portfolio
- Track Investments: Use spreadsheets, brokerage apps
- Set Financial Goals: Short-term and long-term planning
- Use Tools: Portfolio trackers, investment apps, market news alerts
Advanced Topics for Beginners to Explore
- How to Invest in IPOs: Users can apply to invest in an IPO through their stock broker, or brokerage apps.
- Understanding Fundamental and Technical Analysis
- Other Instruments:
- Bonds: Fixed income from governments or corporates
- ETFs: Basket of assets, traded like stocks
1. Educate Yourself
Before investing, learn the stock market basics, including key concepts like stocks vs shares, types of share markets, and financial terms. This will help you make informed decisions.
2. Set Clear Financial Goals
Define why you want to invest—align your goals with your risk tolerance for long-term wealth building, retirement, or short-term gains.
3. Open a Demat and Trading Account
To buy and sell stocks, you’ll need a Demat account (to hold shares) and a trading account (to conduct transactions). Choose a trusted brokerage that offers easy-to-use platforms.
4. Start Small
Begin with a modest amount that you can afford to lose. Starting small reduces the risk while you gain experience and confidence.
5. Research Stocks
Look into companies you’re interested in. Consider factors like financial health, growth potential, and the industry they belong to.
6. Make Your First Purchase
Once you’ve chosen a stock, use your trading account to make your first purchase. Keep track of the stock’s performance and market conditions.
7. Monitor and Adjust
Regularly review your investments and market trends. Stay informed about news related to your invested companies and adjust your strategy if needed.
8. Consider Long-Term Investing
Stock markets tend to rise over time, making long-term investments more profitable. Frequent buying and selling can lead to higher transaction costs and potential losses.
9. Stay Informed
Keep up-to-date with economic indicators, company announcements, and industry trends. Consult reputable financial news outlets and analysts.
Don’ts of Investing in Stocks if You’re a Beginner
- Don’t Follow the Herd: Just because everyone is buying a particular stock doesn’t mean it’s the right choice for you.
- Don’t Panic Sell: Stock markets go through ups and downs. Selling in panic during a dip can lock in losses.
- Don’t Invest Money You Can’t Afford to Lose: Only invest money that you are comfortable risking in the market.
Risks You Should Be Aware Of
Investing in stocks comes with various risks. As a stock market beginner, understanding these risks can help you navigate the market more effectively:
- Market Risk: The risk of losing money due to fluctuations in the stock market.
- Liquidity Risk: The risk that you won’t be able to sell a stock quickly enough to avoid a loss.
- Company Risk: The risk that a company’s stock price may decline due to poor performance or management issues.
- Economic Risk: External factors like inflation, interest rates, and political instability can affect stock prices.
Mitigating these risks involves careful planning, diversification, and staying informed about market trends.
Trading vs Investing: What’s the Difference?
Understanding the difference between trading and investing is essential for stock market beginners. Trading refers to buying and selling stocks frequently, often within a day. Traders aim to capitalize on short-term market movements and usually rely on technical analysis.
Investing, on the other hand, is a long-term approach. Investors buy and hold onto stocks for years, focusing on the company’s growth and potential. Investing aims to build wealth over time through capital appreciation and dividends.
Both strategies have pros and cons; the choice depends on your risk tolerance, time commitment, and financial goals.
Types of Share Market
The share market can be broadly categorized into two:
- Primary Market: This is where companies offer new stocks to the public through Initial Public Offerings (IPOs).
- Secondary Market: Once the stocks are issued, they are traded among investors on stock exchanges like the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and the National Stock Exchange (NSE).
For stock market beginners, starting with the secondary market, where you can buy shares of established companies, is easier.
Stock Exchange for Beginners
A stock exchange for beginners is simply a platform for buying and selling stocks. Popular stock exchanges in India include the BSE and NSE. These exchanges ensure that trading is conducted in a transparent and regulated manner. Learning how the stock exchange operates and familiarizing yourself with its rules is essential for stock market beginners.
Share Market Advisory: Do You Need It?
Navigating the stock market can be challenging for a beginner. Share market advisory services can help guide your decisions. These services provide expert advice on what stocks to buy or sell based on market analysis and company performance. However, it’s important to choose a reliable advisory service and not rely solely on their recommendations. Always do your research before making any investments.
Conclusion
The stock market for beginners can seem complex, but by understanding the basics, knowing when and how to invest, familiarizing yourself with financial terms, and being aware of the risks, you can make informed decisions. Remember to start small, diversify your portfolio, and be patient. The stock market offers opportunities for wealth creation, but it requires a disciplined and informed approach.
Whether you’re exploring trading vs investing or seeking guidance from a share market advisory, always prioritize your financial goals and risk tolerance.
Recap of Key Stock Market Basics
The share market for beginners is a platform to buy and sell shares, tiny ownership units in companies. Key concepts include understanding stock exchanges (NSE, BSE), types of stocks, market orders, and indicators like Sensex and Nifty. Grasping these basics builds a strong foundation for smart investing.
The Importance of Starting Early and Staying Informed
Starting early allows your investments to benefit from compounding over time. Staying informed through financial news, market updates, and analysis helps you adapt your strategy and make better decisions in a changing market.
How to Continuously Learn and Improve Your Investing Skills
Learning doesn’t stop after your first trade. Read investment books, explore courses, follow market trends, and analyze your portfolio regularly. Over time, your skills and confidence as an investor will grow.
*Disclaimer Note: The securities quoted, if any, are for illustration only and are not recommendatory. This article is for education purposes only and shall not be considered as recommendation or investment advice by Research & Ranking. We will not be liable for any losses that may occur. Investment in securities market are subject to market risks. Read all the related documents carefully before investing. Registration granted by SEBI, membership of BASL, and certification from NISM in no way guarantee the performance of the intermediary or provide any assurance of returns to investors.
Related Posts
FAQ
What is the best time to invest in the stock market as a beginner?
There’s no definitive “best time” to invest in the stock market. Historically, long-term investors have benefitted from staying invested, regardless of short-term market fluctuations. It’s often recommended to start investing as early as possible to take advantage of compound interest. However, it’s also essential to know the financial terms, research, and understand the current market conditions to make informed decisions.
How do I choose the right stocks to invest in?
Choosing the right stocks involves research, analysis, and investing based on your risk tolerance. Consider factors such as the company’s financial health, industry trends, management team, and valuation. Diversifying your portfolio across different sectors can also mitigate risk. Additionally, consider consulting with a financial advisor for personalized guidance.
What are the risks associated with investing in the stock market?
Investing in the stock market involves risks, including the potential for capital loss. Market fluctuations, economic downturns, and company-specific factors can all impact stock prices. It’s important to be aware of these risks and to have a well-thought-out investment strategy.
What is the best way for beginners to start investing in the stock market?
Begin with basic education, open a Demat/trading account, and start with mutual funds or blue-chip stocks.
How much money should I invest in the stock market as a beginner?
Only invest money you can afford to lose. Start with a small amount and increase as you gain experience.
What are the basic terms every beginner should know in the stock market?
Understand shares, P/E ratio, dividends, market cap, limit orders, and diversification.
Is stock market investing risky for beginners?
Yes, if done without research. However, with knowledge and a cautious approach, risks can be managed.
How can I minimize risk in the stock market?
Diversify your investments, set stop-losses, and invest for the long term rather than chasing quick gains.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 4 / 5. Vote count: 1
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.