Fundamental Analysis of Stocks – Blog Category
Fundamental analysis of stocks based on the quarterly and annual reports of the companies.
Summary Gautam Adani’s rise to become one of India’s most successful industrialists in recent years can be traced back to […]
Summary The rise of Polycab India is inspiring by all means and shows the aspirational spirit of the Indians and […]
Summary IndusInd Bank started under the leadership of Mr. S.P. Hinduja to serve the NRI community. Today, IndusInd is the […]
Introduction Sona BLW is a prominent Indian company with a global presence that manufactures differential gears, motors, and other components. […]
Introduction Since independence, Tata Steel and SAIL (The Steel Authority of India Limited) have played a key role in the […]
Introduction The Indian Pharmaceutical Industry is one of the world’s largest in terms of production by volume and value. It […]
Introduction Over the last decade, the share of credit disbursed to and by NBFCs in India has experienced significant growth, […]
Introduction This Bank started as an NGO, became an NBFC, and finally became a universal bank. Driven by the philosophy […]
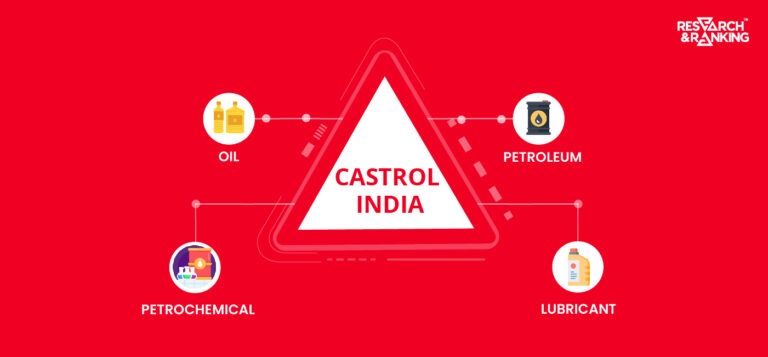
Introduction Talk about lubricants, and Castrol is one brand that immediately comes to mind. This 100-year-old brand is the market […]
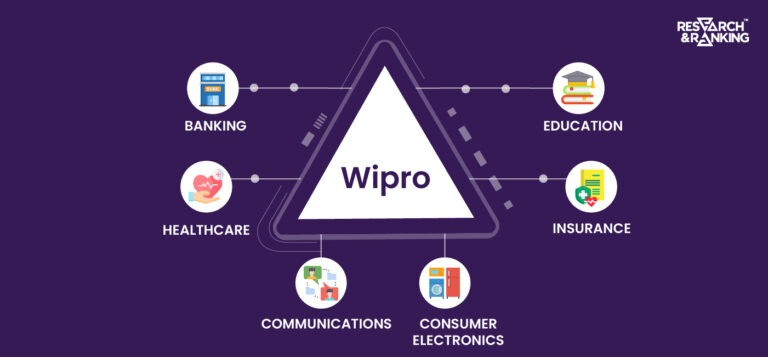
Introduction Wipro is no ordinary company, taking its first step on its journey in 1945 when the world was recovering […]
Frequently asked questions
Get answers to the most pertinent questions on your mind now.
What is an Investment Advisory Firm?
An investment advisory firm is a company that helps investors make decisions about buying and selling securities (like stocks) in exchange for a fee. They can advise clients directly or provide advisory reports and other publications about specific securities, such as high growth stock recommendations. Some firms use both methods, like Research & Ranking, India’s leading stock advisory company, specializing in smart investments and long-term stocks since 2015.
Do we have SEBI registration as an Investment Advisory?
An investment advisory firm is a company that helps investors make decisions about buying and selling securities (like stocks) in exchange for a fee. They can advise clients directly or provide advisory reports and other publications about specific securities, such as high growth stock recommendations. Some firms use both methods, like Research & Ranking, India’s leading stock advisory company, specializing in smart investments and long-term stocks since 2015.
Why choose a SEBI Registered Investment Advisor?
An investment advisory firm is a company that helps investors make decisions about buying and selling securities (like stocks) in exchange for a fee. They can advise clients directly or provide advisory reports and other publications about specific securities, such as high growth stock recommendations. Some firms use both methods, like Research & Ranking, India’s leading stock advisory company, specializing in smart investments and long-term stocks since 2015.
What is the Role of an Investment/Stock Market Advisory Firm in India?
An investment advisory firm is a company that helps investors make decisions about buying and selling securities (like stocks) in exchange for a fee. They can advise clients directly or provide advisory reports and other publications about specific securities, such as high growth stock recommendations. Some firms use both methods, like Research & Ranking, India’s leading stock advisory company, specializing in smart investments and long-term stocks since 2015.